在YoLo-V3中使用Darknet53这个网络结构。下图为Darknet-53的网络结构,加入了残差块的结构。
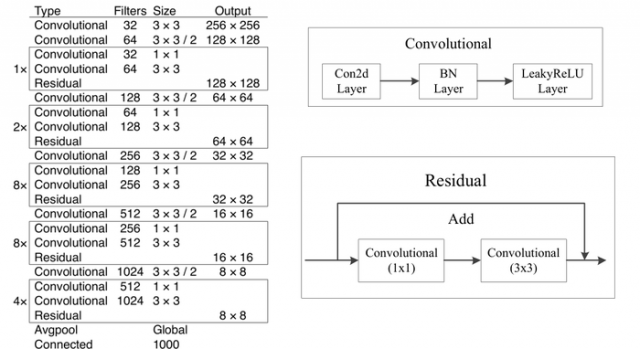
Yolo-V3中的改进:
(1)多尺度计算,Yolo-V3又3个不同特征尺度的输出(使用的是CoCo数据集),分别是13×13×225,26×26×225,52×52×225,这里借鉴了FPN的思想不仅在每个特征图上分别独立做预测,同时通过将小特征图上采样到与大的特征图大小相同,然后与大的特征图拼接做进一步预测。
(2)Yolo-V3代价函数修改,Yolo-v3对类别预测的代价函数进行了修改,没有收用softmax函数,因为原来的分类网络中使用softmax层都是假设一张图片或一个object只属于一个类别,但是在一些复杂的场景下,一个object可能属于多个类,那么在使用softmax可能就会导致漏掉一些类别,所以在Yolo-V3中使用逻辑回归层来对每个类别做二分类,因此当一张图像经过特征提取后的某一类输出如果大于0.5那么就属于这个类。这样一个框就可以预测多个类别。
在Yolo-V3中的维度聚类:
Yolo-V3中使用了k-means聚类计算anchor,聚类的目的是让anchor和邻近的ground truth有更大的IOU,这和anchor的尺寸没有直接的关系。
(1)使用聚类原始数据只有标签框的检测数据集,Yolo-V3都会生成一个包含标注框位置和类别的.txt文件,其中每行都包含(xi,yi,wi,hi)即ground truth相对于原图的坐标。
(2)首先给定k个聚类中心点(wi,hi),这里wi,hi是anchor的宽和高,由于anchor位置不固定,所以没有(x,y)坐标, 只有宽和高。
(3)计算每个标注框和每个聚类中心的距离,d=1-IOU(标注框,聚类中心),这里在计算时将每个标注框的中心点都与聚类中心重合,然后计算IOU,将标注框分配给"距离"最近的聚类中心
(4)所有标注框分配完毕后,对每个族重新计算聚类中心,wi' = 1/Ni∑wi,hi'=1/Ni∑hi,Ni是第i个族的标注框个数,其实就是求该族中所有标注框宽和高的平均值,然后重复3,4步知道聚类中心变化很小。
网络结构(返回3个尺度的输出)
from keras.layers import BatchNormalization from keras.layers.advanced_activations import LeakyReLU from keras.layers import Conv2D,ZeroPadding2D,Add,UpSampling2D,Concatenate from keras.regularizers import l2 def conv(x,*args,**kwargs): new_kwargs = {"kernel_regularizer":l2(5e-4),"use_bias":False} new_kwargs["padding"] = "valid" if kwargs.get("strides")==(2,2) else "same" new_kwargs.update(kwargs) x =Conv2D(*args,**new_kwargs)(x) return x def CBL(x,*args,**kwargs): x = conv(x,*args,**kwargs) x = BatchNormalization()(x) x = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.1)(x) return x def PCBL(x,num_filters): x = ZeroPadding2D(((1,0),(1,0)))(x) x = CBL(x,num_filters,(3,3),strides=(2,2)) return x def CBLR(x,num_filters): y = CBL(x,num_filters,(1,1)) y = CBL(y,num_filters*2,(3,3)) x = Add()([x,y]) return x def CBL5(x,num_filters): x =CBL(x,num_filters,(1,1)) x =CBL(x,num_filters*2,(3,3)) x =CBL(x,num_filters,(1,1)) x =CBL(x,num_filters*2,(3,3)) x =CBL(x,num_filters,(1,1)) return x def CBLC(x,num_filters,out_filters): x =CBL(x,num_filters*2,(3,3)) x =conv(x,out_filters,(1,1)) return x def CBLU(x,num_filters): x = CBL(x,num_filters,(1,1)) x =UpSampling2D(2)(x) return x def body(inputs,num_anchors,num_classes): out=[] x = CBL(inputs,32,(3,3)) n = [1,2,8,8,4] for i in range(5): x = PCBL(x,2**(6+i)) for _ in range(n[i]): x = CBLR(x,2**(5+i)) if i in [2,3,4]: out.append(x) x1 = CBL5(out[2],512) y1 = CBLC(x,512,num_anchors*(num_classes+5)) x = CBLU(x1,256) x = Concatenate()([x,out[1]]) x2 = CBL5(x,256) y2 = CBLC(x2,256,num_anchors*(num_classes+5)) x = CBLU(x2,128) x =Concatenate()([x,out[0]]) x3 = CBL5(x,128) y3 = CBLC(x3,128,num_anchors*(num_classes+5)) return [y3,y2,y1]
从数据集中的xml文件中获取x,y,w,h,label的信息.
import numpy as np from xml.etree.ElementTree import parse class PascalVocXmlParser(object): def __init__(self): pass def get_fname(self,annotation_file): root = self._root_tag(annotation_file) return root.find("filename").text def get_width(self,annotation_file): tree = self._tree(annotation_file) for elem in tree.iter(): print(elem) if "width" in elem.tag: return float(elem.text) def get_height(self,annotation_file): tree = self._tree(annotation_file) for elem in tree.iter(): if "height" in elem.tag: return float(elem.text) def get_labels(self,annotation_file): root = self._root_tag(annotation_file) labels=[] obj_tags =root.findall("object") for t in obj_tags: labels.append(t.find("name").text) return labels def get_boxes(self,annotation_file): root = self._root_tag(annotation_file) bbs=[] obj_tags = root.findall("object") for t in obj_tags: box_tag = t.find("bndbox") x1 = box_tag.find("xmin").text y1 = box_tag.find("ymin").text x2 = box_tag.find("xmax").text y2 = box_tag.find("ymax").text box = np.array([float(x1),float(x2),float(y1),float(y2)]) bbs.append(box) bbs = np.array(bbs) return bbs #获取所有根节点 def _root_tag(self,fname): tree = parse(fname) root = tree.getroot() return root def _tree(self,fname): tree = parse(fname) return tree
根据从xml文件中获得的信息求ytrue
import numpy as np import os from PIL import Image from nets.YoLo_v3_get_xml import PascalVocXmlParser #根据xml文件获取文件名,图片大小,label,box的信息 def get_parse(ann_fname,input_size): parser = PascalVocXmlParser() fname = parser.get_fname(ann_fname) weight = parser.get_width(ann_fname) height = parser.get_height(ann_fname) labels = parser.get_labels(ann_fname) boxes = parser.get_boxes(ann_fname) for i in range(len(boxes)): boxes[i][0] = boxes[i][0]/weight*input_size boxes[i][1] = boxes[i][1]/weight*input_size boxes[i][2] = boxes[i][2]/height*input_size boxes[i][3] = boxes[i][3]/height*input_size return fname,labels,boxes #计算IOU def get_IOU(box1,box2): w_min = min(box1[1],box2[1]) h_min = min(box1[3],box2[3]) w = w_min-box2[0] h = h_min-box1[2] intersect = w*h merge = (box1[1]-box1[0])*(box1[3]-box1[2]) +(box2[1]-box2[0])*(box2[3]-box2[2]) IOU = intersect/(merge-intersect) return IOU #把box和anchor一个点对齐计算IOU #计算anchor和ground truth的最大IOU的位置。 def get_anchor(anchors,box): IOUList = [] anchorslist =np.zeros(((len(anchors)),4),dtype="float32") for i in range(len(anchorslist)): anchorslist[i][0] = box[0] anchorslist[i][1] = anchorslist[i][0] + anchors[i][0] anchorslist[i][2] = box[2] anchorslist[i][3] = anchorslist[i][2] + anchors[i][1] IOU = get_IOU(box,anchorslist[i]) IOUList.append(IOU) anchor =IOUList.index((max(IOUList))) return anchor def get_img(img_dir,fname,input_size): img_fname =os.path.join(img_dir,fname) image = Image.open(img_fname) image = image.resize((input_size,input_size)) image = np.array(image,dtype="float32") image /=255. return image #anchor共有9个,每个尺度3个 def get_ytrue(boxes,anchors,anchor_shape,b,pattern_shape,input_size,classes,labels,ytrues): newbox = np.zeros((4), dtype="float32") for i in range(len(boxes)): #计算出所有anchor与ground truth的最大IOU的index anchor = get_anchor(anchors,boxes[i]) #计算出anchor属于哪个尺度 layer_anchor = anchor//anchor_shape[1] #计算anchor属于该尺度的哪个w,h box_anchor = anchor%anchor_shape[1] rate = pattern_shape[layer_anchor]/input_size cent_x = (boxes[i][0]+boxes[i][1])/2*rate cent_y = (boxes[i][2]+boxes[i][3])/2*rate #向下取整 x = np.floor(cent_x).astype("int32") y = np.floor(cent_y).astype("int32") w = boxes[i][1]-boxes[i][0] h = boxes[i][3]-boxes[i][2] #类别 c = classes.index(labels[i]) newbox[0] = cent_x newbox[1] = cent_y newbox[2] = np.log(max(w,1))/anchors[anchor][0] newbox[3] = np.log(max(h,1))/anchors[anchor][1] #获得ytrue ytrues[layer_anchor][b,x,y,box_anchor,0:4] = newbox[0:4] ytrues[layer_anchor][b,x,y,box_anchor,4] =1 ytrues[layer_anchor][b,x,y,box_anchor,5+c] =1 return ytrues #数据生成器 def generator(batch_size,classes,ann_fnames,img_dir,input_size,anchors): pattern_shape = [52, 26, 13] anchor_shape=[3,3] n = len(ann_fnames) i = 0 while True: inputs = [] ytrues = [np.zeros((batch_size, pattern_shape[l], pattern_shape[l], anchor_shape[1], 5 + len(classes))) for l in range(3)] #构造一个batch_size for b in range(batch_size): if i == 0: np.random.shuffle(ann_fnames) fname, labels, boxes = get_parse(ann_fnames[i], input_size) ytrues = get_ytrue(boxes,anchors,anchor_shape,b,pattern_shape,input_size,classes,labels,ytrues) img = get_img(img_dir, fname, input_size) inputs.append(img) i = (i + 1) % n inputs = np.array(inputs) #返回一个batch_size yield inputs,[ytrues[2],ytrues[1],ytrues[0]]
计算loss
Yolo-V3采用直接位置预测,就是预测边界框中心点相对于对应cell左上角的相对位置偏移,为了将边界框中心点约束在当前cell中,使用sigmoi函数 处理偏移值,这样预测的偏移值在(0,1)范围内。在Faster-RCNN中不加任何限制就会导致不管初始的bbox在图像的什么位置,通过预测偏移量可以将bbox移动到图像任何位置。
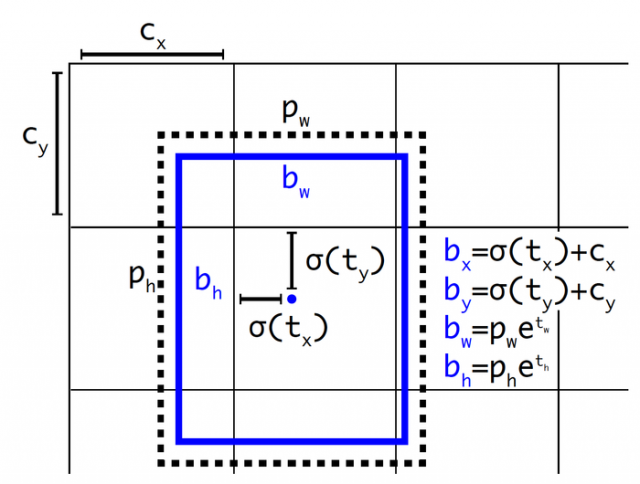
loss组成
#计算回归loss def get_loss_box(ytrue,ypre,box_scale,object_mask): xy_delta = box_scale * object_mask * (ypre[...,:2]-ytrue[...,:2]) wh_delta = box_scale * object_mask * (tf.sqrt(ypre[...,2:4])-tf.sqrt(ytrue[...,2:4])) loss_xy = K.sum(K.square(xy_delta),list(range(1,5))) loss_wh = K.sum(K.square(wh_delta),list(range(1,5))) return loss_xy+loss_wh #计算置信度loss def get_loss_con(ytrue,ypre,noobj_scale,object_mask,IOU): object_mask = K.squeeze(object_mask,axis=-1) con_delta = object_mask * (ypre*IOU-ytrue) + noobj_scale * (1-object_mask)*(ypre*IOU-ytrue) loss_con = K.sum(K.square(con_delta),list(range(1,4))) return loss_con #计算类别loss def get_loss_c(ytrue,ypre,object_mask): ytrue = tf.cast(ytrue,tf.int64) loss_class = object_mask*tf.expand_dims(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(labels=ytrue,logits=ypre),4) return loss_class def lossCalculator(ytrue,ypre,anchors,batch_size,input_size,box_scale,noobj_scale,ignore_thresh): #ypre从网络中得到的shape=(batch_size,13,13,3*(num_classes+5))这里要转换成(batch_size,13,13,3,num_classes+5) ypre = K.reshape(ypre,shape=[-1, ypre.shape[-3], ypre.shape[-2], anchors.shape[0], ypre.shape[-1] // anchors.shape[0]]) ytrue = K.reshape(ytrue, shape=[-1, ypre.shape[1], ypre.shape[2], ypre.shape[3], ypre.shape[4]]) ytrue,ypre = get_ytrue_ypre(ytrue,ypre,anchors,batch_size) object_mask = K.expand_dims(ytrue[...,4],4) IOU = get_IOU(ytrue[...,:4],ypre[...,:4],input_size) loss_box = get_loss_box(ytrue[...,:4],ypre[...,:4],box_scale,object_mask) loss_con = get_loss_con(ytrue[...,4],ypre[...,4],noobj_scale,object_mask,IOU) loss_class = get_loss_c(ytrue[...,5:],ypre[...,5:],object_mask) losses = loss_box+loss_con+loss_class return tf.reduce_mean(losses) def fn_loss(ytrues,ypres): ignore_thresh =0.5 noobj_scale=0.5 box_scale=1 input_size =416 batch_size =1 anchors = np.array([[[10, 13], [16, 30], [33, 23]], [[30, 61], [62, 45], [59, 119]], [[116, 90], [156, 198], [373, 326]]]) losses=[] loss =lossCalculator(ytrues,ypres,anchors[2-ypres.shape[1]//26],batch_size,input_size,box_scale,noobj_scale,ignore_thresh) losses.append(loss) return tf.sqrt(losses)
本文链接:http://task.lmcjl.com/news/12747.html