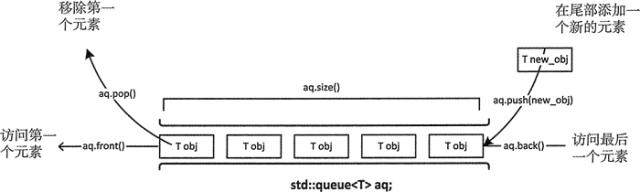
图 1 queue容器
std::queue<std::string> words;也可以使用拷贝构造函数:
std::queue<std::string> copy_words {words}; // A duplicate of words
stack<T>、queue<T> 这类适配器类都默认封装了一个 deque<T> 容器,也可以通过指定第二个模板类型参数来使用其他类型的容器:std::queue<std::string, std::list<std::string>>words;底层容器必须提供这些操作:front()、back()、push_back()、pop_front()、empty() 和 size()。
std::deque<double> values {1.5, 2.5, 3.5, 4.5}; std::queue<double> numbers(values);
while (!numbers, empty())
{
std ::cout << numbers. front() << " "; // Output the 1st element
numbers. pop(); // Delete the 1st element
}
std::cout << std::endl;
用循环列出 numbers 的内容,循环由 empty() 返回的值控制。调用 empty() 可以保证我们能够调用一个空队列的 ftont() 函数。如代码所示,为了访问 queue 中的全部元素,必须删除它们。如果不想删除容器中的元素,必须将它们复制到另一个容器中。如果一定要这么操作,我们可能需要换一个容器。
// Defines a customer by their time to checkout
#ifndef CUSTOMER_H
#define CUSTOMER_H
class Customer
{
protected:
size_t service_t {}; // Time to checkout
public:
explicit Customer(size_t st = 10) :service_t {st}{}
// Decrement time remaining to checkout
Customer& time_decrement()
{
if (service_t > 0)
--service_t;
return *this;
}
bool done() const { return service_t == 0; }
};
#endif
这里只有一个成员变量 service_t,用来记录顾客结账需要的时间。每个顾客的结账时间都不同。每过一分钟,会调用一次 time_decrement() 函数,这个函数会减少 service_t 的值,它可以反映顾客结账所花费的时间。当 service_t 的值为 0 时,成员函数 done() 返回 true。
// Supermarket checkout - maintains and processes customers in a queue
#ifndef CHECKOUT_H
#define CHECKOUT_H
#include <queue> // For queue container
#include "Customer.h"
class Checkout
{
private:
std::queue<Customer> customers; // The queue waiting to checkout
public:
void add(const Customer& customer) { customers.push(customer); }
size_t qlength() const { return customers.size(); }
// Increment the time by one minute
void time_increment()
{
if (!customers.empty())
{ // There are customers waiting...
if (customers.front().time_decrement().done()) // If the customer is done...
customers.pop(); // ...remove from the queue
}
};
bool operator<(const Checkout& other) const { return qlength() < other.qlength(); }
bool operator>(const Checkout& other) const { return qlength() > other.qlength(); }
};
#endif
这相当于自我解释。queue 容器是 Checkout 唯一的成员变量,用来保存等待结账的 Customer 对象。成员函数 add() 可以向队列中添加新顾客。只能处理队列中的第一个元素。 每过一分钟,调用一次 Checkout 对象的成员函数 time_increment(},它会调用第一个 Customer 对象的成员函数 time_decrement() 来减少剩余的服务时间,然后再调用成员函数 done()。如果 done() 返回 true,表明顾客结账完成,因此把他从队列中移除。Checkout 对象的比较运算符可以比较队列的长度。
std::uniform_int_distribution<> d {10, 100};
这里只定义了分布对象 d,它指定了整数值分布的范围。为了获取这个范围内的随机数,我们需要使用一个随机数生成器,然后把它作为参数传给 d 的调用运算符,从而返回一个随机整数。 random 头文件中定义了几种随机数生成器。这里我们使用最简单的一个,可以按如下方式定义:std::random_device random_number_engine;为了在 d 分布范围内生成随机数,我们可以这样写:
auto value = d(random_number_engine); // Calls operator()() for dvalue 的值在 d 分布范围内。
// Simulating a supermarket with multiple checkouts #include <iostream> // For standard streams #include <iomanip> // For stream manipulators #include <vector> // For vector container #include <string> // For string class #include <numeric> // For accumulate() #include <algorithm> // For min_element & max_element #include <random> // For random number generation #include "Customer.h" #include "Checkout.h" using std::string; using distribution = std::uniform_int_distribution<>; // Output histogram of service times void histogram(const std::vector<int>& v, int min) { string bar (60, '*'); // Row of asterisks for bar for (size_t i {}; i < v.size(); ++i) { std::cout << std::setw(3) << i+min << " " // Service time is index + min << std::setw(4) << v[i] << " " // Output no. of occurrences << bar.substr(0, v[i]) // ...and that no. of asterisks << (v[i] > static_cast<int>(bar.size()) ? "...": "") << std::endl; } } int main() { std::random_device random_n; // Setup minimum & maximum checkout periods - times in minutes int service_t_min {2}, service_t_max {15}; distribution service_t_d {service_t_min, service_t_max}; // Setup minimum & maximum number of customers at store opening int min_customers {15}, max_customers {20}; distribution n_1st_customers_d {min_customers, max_customers}; // Setup minimum & maximum intervals between customer arrivals int min_arr_interval {1}, max_arr_interval {5}; distribution arrival_interval_d {min_arr_interval, max_arr_interval}; size_t n_checkouts {}; std::cout << "Enter the number of checkouts in the supermarket: "; std::cin >> n_checkouts; if (!n_checkouts) { std::cout << "Number of checkouts must be greater than 0. Setting to 1." << std::endl; n_checkouts = 1; } std::vector<Checkout> checkouts {n_checkouts}; std::vector<int> service_times(service_t_max-service_t_min+1); // Add customers waiting when store opens int count {n_1st_customers_d(random_n)}; std::cout << "Customers waiting at store opening: " << count << std::endl; int added {}; int service_t {}; while (added++ < count) { service_t = service_t_d(random_n); std::min_element(std::begin(checkouts), std::end(checkouts))->add(Customer(service_t)); ++service_times[service_t - service_t_min]; } size_t time {}; // Stores time elapsed const size_t total_time {600}; // Duration of simulation - minutes size_t longest_q {}; // Stores longest checkout queue length // Period until next customer arrives int new_cust_interval {arrival_interval_d(random_n)}; // Run store simulation for period of total_time minutes while (time < total_time) // Simulation loops over time { ++time; // Increment by 1 minute // New customer arrives when arrival interval is zero if (--new_cust_interval == 0) { service_t = service_t_d(random_n); // Random customer service time std::min_element(std::begin(checkouts), std::end(checkouts))->add(Customer(service_t)); ++service_times[service_t - service_t_min]; // Record service time // Update record of the longest queue occurring for (auto & checkout : checkouts) longest_q = std::max(longest_q, checkout.qlength()); new_cust_interval = arrival_interval_d(random_n); } // Update the time in the checkouts - serving the 1st customer in each queue for (auto & checkout : checkouts) checkout.time_increment(); } std::cout << "Maximum queue length = " << longest_q << std::endl; std::cout << "\nHistogram of service times:\n"; histogram(service_times, service_t_min); std::cout << "\nTotal number of customers today: " << std::accumulate(std::begin(service_times), std::end(service_times), 0) << std::endl; }
Enter the number of checkouts in the supermarket: 3
Customers waiting at store opening: 19
Maximum queue length = 10
Histogram of service times:
2 16 ****************
3 15 ***************
4 12 ************
5 11 ***********
6 17 *****************
7 20 ********************
8 18 ******************
9 16 ****************
10 10 **********
11 12 ************
12 16 ****************
13 21 *********************
14 17 *****************
15 21 *********************
Total number of customers today: 222
本文链接:http://task.lmcjl.com/news/15944.html