template <typename T, typename Container=std::vector<T>, typename Compare=std::less<T>> class priority_queue如你所见,priority_queue 实例默认有一个 vector 容器。函数对象类型 less<T> 是一个默认的排序断言,定义在头文件 function 中,决定了容器中最大的元素会排在队列前面。fonction 中定义了 greater<T>,用来作为模板的最后一个参数对元素排序,最小元素会排在队列前面。当然,如果指定模板的最巵一个参数,就必须提供另外的两个模板类型参数。
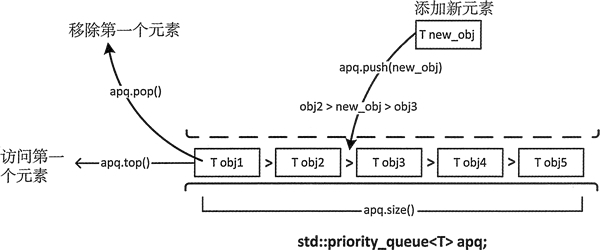
图 1
std::priority_queue<std::string> words;可以用适当类型的对象初始化一个优先级队列:
std::string wrds[] { "one", "two", "three", "four"};
std::priority_queue<std::string> words { std::begin(wrds),std:: end(wrds)}; // "two" "three" "one" "four"
初始化列表中的序列可以来自于任何容器,并且不需要有序。优先级队列会对它们进行排序。
std::priority_queue<std::string> copy_words {words}; // copy of words
也有带右值引用参数的拷贝构造函数,它可以移动一个实参对象。
std:: string wrds[] {"one", "two", "three", "four"};
std::priority_queue<std::string, std::vector<std::string>,std: :greater<std::string>> words1 {std::begin (wrds) , std:: end (wrds) }; //"four" "one" "three" "two"
这会通过使用 operator>() 函数对字符串对象进行比较,进而生成一个优先级队列,因此这会和它们在队列中的顺序相反。
std::string wrds [] {"one", "two", "three", "four"};
std::priority_queue<std::string, std::deque<std::string>> words {std::begin(wrds), std::end(wrds)};
这个 words 优先级队列在 deque 容器中保存了一些 wrds 数组中的字符串,这里使用默认的比较断言,因此队列中的元素会和上面 word1 中元素的顺序相同。priority_queue 构造函数会生成一个和第二个类型参数同类型的容器来保存元素,这也是 priority_queue 对象的底层容器。
std::vector<int> values{21, 22, 12, 3, 24, 54, 56};
std::priority_queue<int> numbers {std::less<int>(),values};
priority_queue 构造函数的第一个参数是一个用来对元素排序的函数对象,第二个参数是一个提供初始元素的容器。在队列中用函数对象对 vector 元素的副本排序。values 中元素的顺序没有变,但是优先级队列中的元素顺序变为:56 54 24 22 21 12 3。优先级队列中用来保存元素的容器是私有的,因此只能通过调用 priority_queue 对象的成员函数来对容器进行操作。构造函数的第一个参数是函数对象类型,它必须和指定的比较模板类型参数相同,函数对象类型默认是 less<T>。如果想使用不同类型的函数,需要指定全部的模板类型参数。例如:
std::priority_queue<int, std::vector<int>,std::greater<int>> numbersl {std::greater<int>(), values};
第三个类型参数是一个比较对象类型。如果要指定这个参数,必须指定前两个参数——元素类型和底层容器类型。
std::priority_queue<std::string> words;
std::string word; std::cout << "Enter words separated by spaces, enter Ctrl+Z on a separate line to end:\n";
while (true)
{
if ((std::cin >> word).eof())
break;
words.push(word);
}
按下 Ctrl+Z 组合键会在输入流中设置文件结束状态,因此可以用来结束循环输入。istream 对象的成员函数 operator>>() 返回一个输入流对象,因此我们可以用 if 条件表达式来调用 eof() 以检查 cin 的状态。这里会对输入单词进行排序,所以最大的单词总在 words 队列的前面——自动对输入单词排序。
std::priority_queue<std::string> words_copy {words}; // A copy for output
while (!words_copy.empty())
{
std:: cout << words_copy.top () <<" ";
words_copy.pop();
}
std::cout << std::endl;
这里首先生成了一个 words 的副本,因为输出 words 会移除它的内容。输出 top() 返回的元素后,我们需要使用 pop() 来使下一个元素可访问。移除全部元素后,在循环条件中调用 empty() 以结束循环。也可以使用表达式 words_copy.size() 来控制循环,因为返回值会被隐式转换为布尔值,这样在 size() 返回 0 时,表达式的结果为 false。
one two three four five six seven
^Z
two three six seven one four five
当然,如果需要多次输出 priority_queue 的内容,最好定义一个函数。这个函数应该是通用的,如下所示:
template<typename T>
void list_pq(std::priority_queue<T> pq, size_t count = 5)
{
size_t n{count};
while (!pq. empty())
{
std::cout << pq. top() << " ";
pq.pop();
if (--n) continue;
std::cout << std::endl;
n = count;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
参数是以传值方式传入的,因此这里会处理一个优先级队列的副本。它是一个适用于任何类型容器的函数模板,只要容器实现了用于向 ostream 输出的 operator<<() 函数。如果没有设置第二个参数,默认每 5 个输出值一行。当然也可以定义一个适用于 queue 容器适配对象的函数模板。可以如下所示使用 priority_queue 的成员函数 emplace():
words.emplace("nine");
以字符串为参数调用 string 类的构造函数会在容器的适当位置生成一个对象。这比下面的语句更有效率:
words.push("nine");
这里编译器会在字符文字处插入一个 string 构造函数来生成 push() 的参数,然后以这个临时 string 对象作为参数调用 push()。push() 函数然后会调用 string 类的拷贝构造函数来将生成对象添加到容器中。我们把这些代码段组织成一个完整的程序:// Exercising a priority queue container adapter #include <iostream> // For standard streams #include <queue> // For priority_queue<T> #include <string> // For string class using std::string; // List contents of a priority queue template<typename T> void list_pq(std::priority_queue<T> pq, size_t count = 5) { size_t n {count}; while (!pq.empty()) { std::cout << pq.top() << " "; pq.pop(); if (--n) continue; std::cout << std::endl; n = count; } std::cout << std::endl; } int main() { std::priority_queue<std::string> words; std::string word; std::cout << "Enter words separated by spaces, enter Ctrl+Z on a separate line to end:\n"; while (true) { if ((std::cin >> word).eof()) break; words.push(word); } std::cout << "You entered " << words.size() << " words:" << std::endl; list_pq(words); }运行结果为:
Enter words separated by spaces, enter Ctrl+Z on a separate line to end:
one two three four five six seven eight nine ten eleven twelve
^Z
You entered 12 words:
two twelve three ten six
seven one nine four five
eleven eight
本文链接:http://task.lmcjl.com/news/13982.html